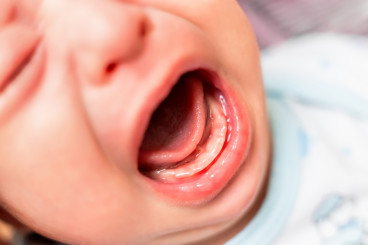
Areas of the Oral Cavity
The oral cavity is a complex and multifaceted region of the human body, comprising several distinct areas that work together to facilitate vital functions such as eating, drinking, speech, and oral hygiene. Understanding the anatomy and purpose of these areas is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Areas Explained
The oral cavity begins at the lips and extends posteriorly to the oropharynx, which is the opening to the throat. This expansive region can be divided into several key areas, each with its own unique characteristics and functions.
Lips
The lips are the outermost, visible part of the oral cavity. They are composed of muscle, connective tissue, and skin, and play a crucial role in speech, facial expression, and the initial stages of the digestive process. The upper and lower lips are referred to as the maxillary and mandibular lips, respectively.
Vestibule
The vestibule is the space between the lips/cheeks and the teeth and gums. It is divided into the maxillary and mandibular vestibules, which allow for the movement of the lips and cheeks during speech, chewing, and other oral functions.
Oral Mucosa
The oral mucosa is the moist, pink lining that covers the majority of the oral cavity. It is composed of specialized epithelial cells that protect the underlying tissues from the various substances and microorganisms present in the mouth. The oral mucosa is divided into several regions, including the gingiva (gums), the tongue, the floor of the mouth, the hard palate, and the soft palate.
Gingiva
The gingiva, or gums, are the firm, pink tissue that surrounds the base of the teeth. The gingiva helps to protect the teeth and their supporting structures from the external environment, and it also plays a role in the overall health of the mouth.
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ that is essential for taste, speech, and the manipulation of food during chewing and swallowing. It is divided into the body, root, and tip, and it is covered in specialized taste buds that allow us to perceive different flavors.
Floor of the Mouth
The floor of the mouth is the area beneath the tongue, and it is lined with the oral mucosa. This region contains the sublingual salivary glands, which produce saliva that helps to maintain a moist environment in the mouth.
Hard Palate
The hard palate is the bony, anterior portion of the roof of the mouth. It is covered by a keratinized, specialized epithelium that helps to protect the underlying structures.
Soft Palate
The soft palate is the posterior, muscular portion of the roof of the mouth. It is responsible for closing off the nasal cavity during swallowing and speech, and it also helps to direct the flow of air during breathing.
Oropharynx
The oropharynx is the opening at the back of the oral cavity that leads to the throat. It is the transition zone between the oral cavity and the pharynx, and it plays a crucial role in swallowing and the initiation of the digestive process.
Conclusion
In summary, the oral cavity is a complex and multifaceted region that is essential for various vital functions, including eating, drinking, speech, and oral hygiene. Understanding the unique characteristics and purposes of each of the key areas within the oral cavity is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Discover the full scope of your oral health with Dr. BestPrice - the leading dental auction platform for affordable, high-quality treatments.