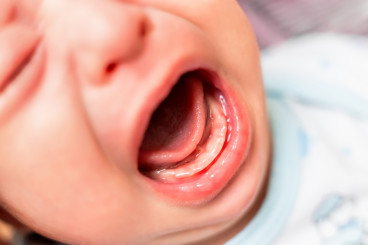
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the mucous membranes within the oral cavity. This condition can manifest in various forms and can involve different areas of the mouth, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, and the roof or floor of the mouth. Stomatitis may present as sores, swelling, redness, and discomfort, and it can significantly impact an individual’s ability to eat, speak, and maintain oral hygiene.
Types of Stomatitis
There are several types of stomatitis, each with distinct characteristics and underlying causes:
Aphthous Stomatitis (Canker Sores): This is the most common form, characterized by small, painful ulcers that appear on the soft tissues inside the mouth. The exact cause is unknown, though it is believed to be linked to stress, hormonal changes, certain food sensitivities, and underlying health conditions.
Herpetic Stomatitis: Caused by the herpes simplex virus, this form results in painful blisters and sores, usually around the lips and mouth. The initial infection often occurs in childhood and may recur during periods of stress or illness.
Contact Stomatitis: This type occurs as a reaction to irritants or allergens. Common triggers include certain dental products, foods, or metals in dental work, leading to localized inflammation and discomfort.
Candida Stomatitis (Oral Thrush): This fungal infection is caused by an overgrowth of the Candida species, resulting in white patches on the tongue and inside the cheeks. It is more common in immunocompromised individuals, those using certain medications, or those with diabetes.
Angular Stomatitis: Characterized by cracks or sores at the corners of the mouth, this type often results from nutrient deficiencies (such as vitamin B12 or iron), frequent lip licking, or ill-fitting dentures.
Symptoms
The symptoms of stomatitis can vary widely depending on the type and severity of the condition, but common signs include:
- Painful sores or ulcers in the mouth
- Redness and swelling of the mucous membranes
- Difficulty eating, swallowing, or speaking
- A burning sensation in the mouth
- Bleeding or crusting at the corners of the mouth (in cases of angular stomatitis)
- White patches or lesions, particularly in cases of candidiasis
Causes
Stomatitis can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Infections: Viral (herpes), bacterial, or fungal infections contribute to the development of stomatitis.
- Irritation: Physical trauma from dental procedures, ill-fitting dentures, or aggressive brushing can lead to inflammation.
- Allergic Reactions: Sensitivities to dental materials, certain foods, or oral hygiene products may provoke stomatitis.
- Systemic Conditions: Diseases such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and nutritional deficiencies can predispose individuals to oral inflammation.
- Stress: Emotional stress has been linked to the occurrence of canker sores and other forms of stomatitis.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of stomatitis typically involves a thorough clinical examination by a dental or healthcare professional. The practitioner will assess the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and any potential triggers. In some cases, laboratory tests may be conducted to identify infections or underlying health issues contributing to stomatitis.
Treatment
The treatment for stomatitis depends on the underlying cause and may include:
Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter topical anesthetics or anti-inflammatory gels can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
Antifungal Medications: In cases of candidiasis, antifungal treatments are prescribed to eliminate the fungal overgrowth.
Antiviral Drugs: For herpetic stomatitis, antiviral medications may be recommended to reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks.
Corticosteroids: These may be prescribed to manage severe inflammation, particularly in cases of aphthous stomatitis.
Nutritional Supplements: Addressing deficiencies in vitamins and minerals may be necessary for certain types of stomatitis.
Prevention
Preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing stomatitis. These include maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding known irritants or allergens, managing stress levels, and ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
Conclusion
Stomatitis is a common and often uncomfortable condition that can affect individuals of all ages. Understanding its various forms, symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve quality of life for those affected.
Explore affordable dental treatments for stomatitis on Dr. BestPrice today!