Dental X-Ray Shielding: ALARA Compliance and Patient/Provider Safety
Dental x-rays are essential for diagnosis, but safety is paramount. This article delves into the importance of proper shielding techniques, ALARA principles, and best practices for protecting patients and dental professionals. Learn about the latest advancements in radiation protection and how to maintain a safe dental environment.
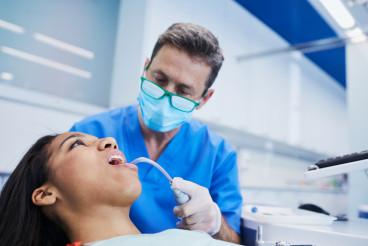
In the realm of modern dentistry, dental x-rays play a crucial role in diagnosis and treatment planning. However, with the use of ionizing radiation comes the responsibility to prioritize safety for both patients and dental professionals. This article explores the critical aspects of dental x-ray shielding, the importance of ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) compliance, and best practices for ensuring patient and provider safety in dental settings.
Understanding Dental X-Rays and Radiation Exposure
Dental x-rays are a type of diagnostic imaging that uses low levels of ionizing radiation to capture images of teeth, gums, and surrounding structures. While these x-rays are essential for detecting dental issues that may not be visible during a regular oral examination, it's important to recognize that even low doses of radiation can potentially have cumulative effects over time.
The amount of radiation exposure from dental x-rays is relatively small compared to other medical imaging procedures. However, the dental community adheres to the ALARA principle to minimize radiation exposure while maintaining diagnostic quality. This principle emphasizes using the lowest radiation dose necessary to achieve the desired diagnostic information.
ALARA Compliance in Dental Practices
ALARA is not just a recommendation; it's a fundamental principle in radiation protection. Dental practices must implement ALARA guidelines to ensure the safety of patients and staff. Here are key aspects of ALARA compliance in dental x-ray procedures:
Justification: Each x-ray should be medically justified based on the patient's specific needs and dental history. Routine x-rays without clinical indication should be avoided.
Optimization: Use the most appropriate imaging technique and equipment to obtain the necessary diagnostic information while minimizing radiation exposure.
Dose Limitation: Implement measures to keep radiation doses as low as possible without compromising image quality.
Equipment Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain x-ray equipment to ensure optimal performance and minimize unnecessary radiation exposure.
Staff Training: Provide comprehensive training to dental professionals on radiation safety, proper equipment use, and shielding techniques.
Shielding Techniques for Patient Protection
Protecting patients from unnecessary radiation exposure is a top priority in dental practices. The following shielding techniques are essential for patient safety:
Lead Aprons: The use of lead aprons is a standard practice in dental offices. These aprons shield the patient's body, particularly the thyroid gland and reproductive organs, from scattered radiation.
Thyroid Collars: In addition to lead aprons, thyroid collars provide specific protection for the thyroid gland, which is particularly sensitive to radiation.
Collimation: Proper collimation of the x-ray beam ensures that only the area of interest is exposed to radiation, reducing unnecessary exposure to surrounding tissues.
Digital Radiography: Switching to digital x-ray systems can significantly reduce radiation exposure compared to traditional film-based systems while providing instant image availability.
Proper Positioning: Correct patient positioning and precise aiming of the x-ray beam minimize the need for retakes, thereby reducing overall radiation exposure.
Age-Appropriate Protocols: Implement specific protocols for pediatric patients, pregnant women, and other sensitive populations to minimize radiation risks.
Provider Safety Measures
Dental professionals who regularly work with x-ray equipment are at risk of cumulative radiation exposure. Implementing the following safety measures is crucial for provider protection:
Distance: Increase distance from the radiation source when possible, as radiation intensity decreases with distance.
Time: Minimize exposure time by efficiently conducting x-ray procedures and utilizing fast image receptors.
Shielding: Use structural shielding, such as lead-lined walls, and personal protective equipment like lead aprons and thyroid collars when necessary.
Dosimetry Monitoring: Regularly monitor radiation exposure levels for dental staff using personal dosimeters.
Education and Training: Provide ongoing education on radiation safety, proper equipment use, and the latest shielding techniques.
Equipment Maintenance: Ensure regular maintenance and calibration of x-ray equipment to prevent radiation leakage and optimize performance.
Advancements in Dental X-Ray Technology
The field of dental radiography continues to evolve, with new technologies aimed at improving image quality while reducing radiation exposure. Some notable advancements include:
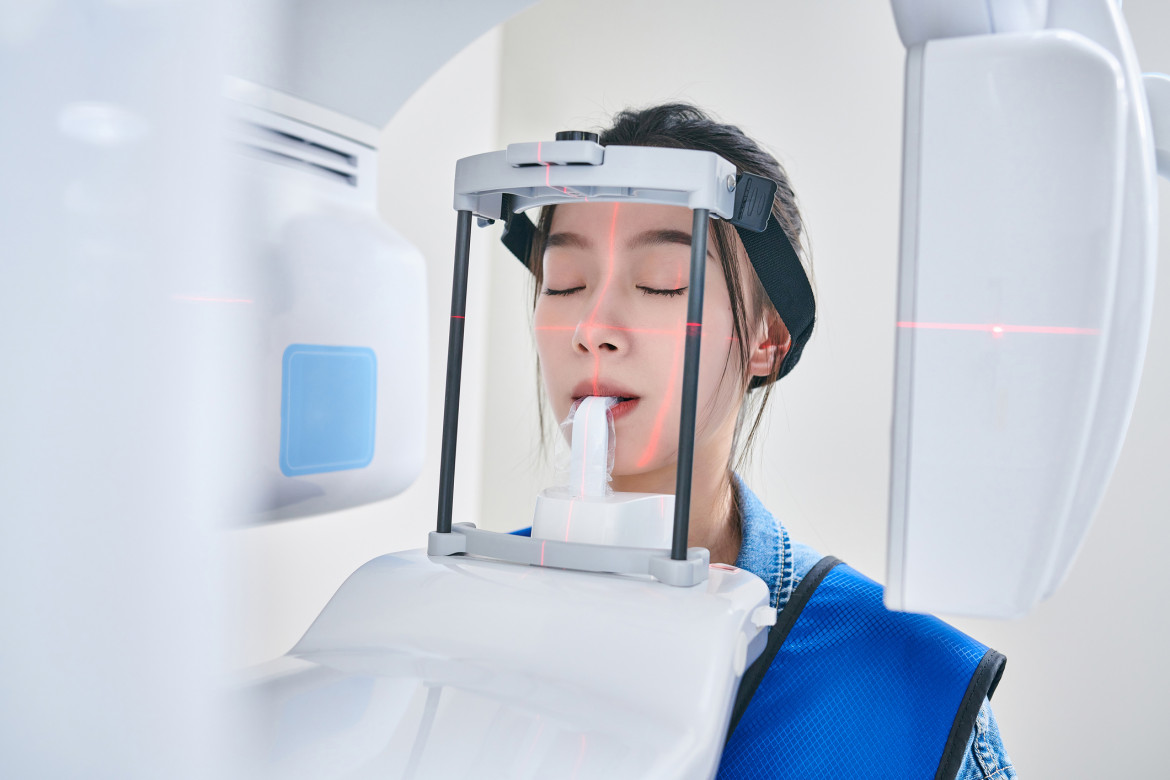
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT): This technology provides 3D imaging with relatively low radiation doses compared to traditional CT scans.
Handheld X-Ray Devices: Portable x-ray units offer flexibility in various clinical settings while incorporating built-in shielding for operator safety.
AI-Assisted Imaging: Artificial intelligence algorithms can enhance image quality, potentially reducing the need for retakes and lowering overall radiation exposure.
Digital Sensors with Higher Sensitivity: Advanced digital sensors require less radiation to produce high-quality images, further reducing patient exposure.
Regulatory Compliance and Best Practices
Dental practices must adhere to regulatory guidelines set forth by organizations such as the American Dental Association (ADA), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and state radiation control programs. Key aspects of regulatory compliance include:
Equipment Registration: Properly register all x-ray equipment with relevant regulatory bodies.
Quality Assurance Programs: Implement comprehensive quality assurance programs to maintain equipment performance and safety standards.
Record Keeping: Maintain accurate records of equipment maintenance, staff training, and patient exposure histories.
Continuing Education: Ensure that all staff members involved in x-ray procedures receive ongoing education on radiation safety and regulatory updates.
Facility Design: Incorporate proper shielding in the design of x-ray rooms to protect adjacent areas from radiation scatter.
Patient Education and Communication
Effective communication with patients about dental x-rays and radiation safety is crucial for building trust and ensuring compliance with safety protocols. Dental practices should:
- Explain the necessity and benefits of dental x-rays in relation to the patient's oral health.
- Address patient concerns about radiation exposure and provide accurate information about the risks and safety measures in place.
- Obtain informed consent before conducting x-ray procedures, especially for pregnant patients or those with specific health concerns.
- Provide clear instructions on the use of protective equipment like lead aprons and thyroid collars.
- Educate patients on the practice's commitment to ALARA principles and ongoing efforts to minimize radiation exposure.
Conclusion
Relevant ADA Dental Codes for dental x-rays:
D0210 - Intraoral - complete series of radiographic images
D0220 - Intraoral - periapical first radiographic image
D0230 - Intraoral - periapical each additional radiographic image
D0240 - Intraoral - occlusal radiographic image
D0270 - Bitewing - single radiographic image
D0272 - Bitewings - two radiographic images
D0274 - Bitewings - four radiographic images
D0330 - Panoramic radiographic image
D0340 - 2D cephalometric radiographic image
D0367 - Cone beam CT capture and interpretation with field of view of both jaws
Dental x-rays remain an indispensable tool in modern dentistry, providing crucial diagnostic information for optimal patient care. By adhering to ALARA principles, implementing robust shielding techniques, and staying informed about technological advancements, dental practices can ensure the safety of both patients and providers while maintaining high standards of care.
As the field of dental radiography continues to evolve, it's essential for dental professionals to stay informed about the latest safety protocols and technologies. By prioritizing radiation safety and continuously improving practices, the dental community can provide the best possible care while minimizing potential risks associated with x-ray exposure.
Need dental x-rays or other dental procedures but worried about the cost? Visit Dr. BestPrice Dental Auction Site to find affordable dental care near you. Our unique dental auction platform connects patients with quality dental providers offering discounted services. Bid on dental treatments and enjoy significant savings on various procedures, including x-rays. Start your journey to a healthier smile without breaking the bank – explore Dr. BestPrice today!